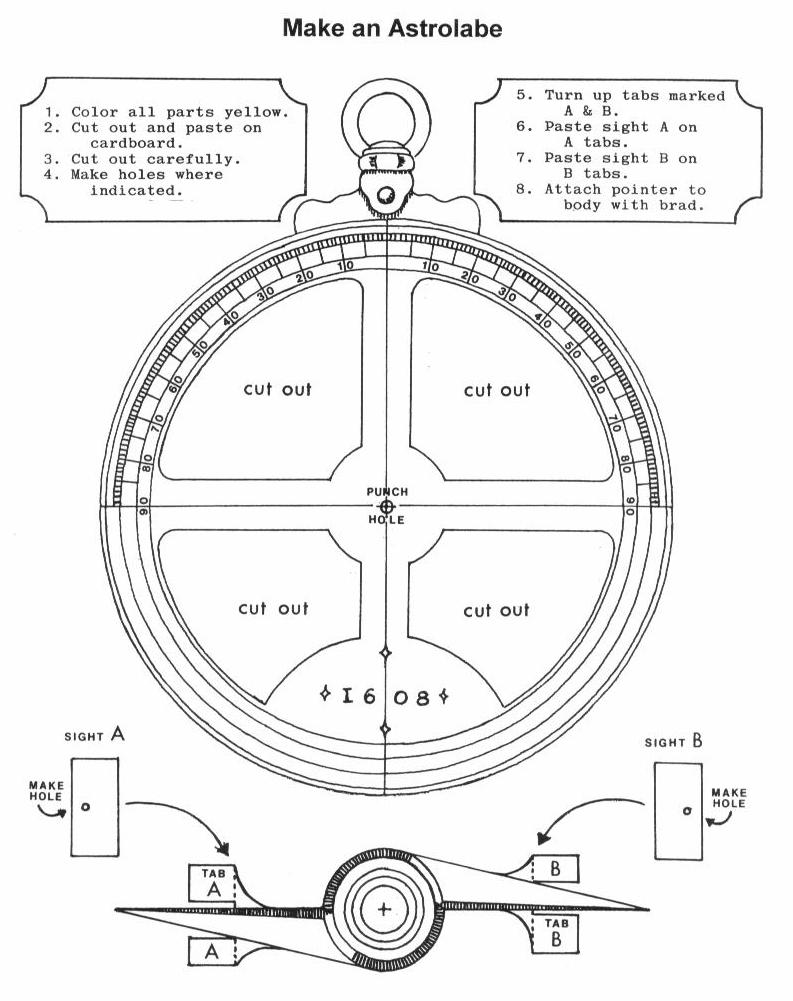
Classroom Activity: The Astrolabe
The astrolabe was an instrument used for the taking of altitudes of
heavenly bodies, from which time and latitude were deductible.The planispheric astrolabe, to which the name is now commonly restricted, is
believed to have been a Greek instrument and may have been invented as
early as 240 B.C. With a history of 2,000 years it may claim to be the
oldest scientific instrument in the world. The Arabic scholars and
mathematicians developed the astrolabe into a precise instrument, which
was capable of indicating time and the placement of heavenly bodies.In its most usual form, the mariner's astrolabe consists of an evenly
balanced circle or disk of metal, hung by a ring and provided with a
rotatable alidade with sights. The alidade, turning within the circle of
degrees marked on the outer edge, was used for measuring the altitudes
of the sun or stars.Seamen from about 1480 to the middle of the 18th century, relied
largely upon such instruments and tables of the sun's declination for
finding latitude.To reduce wind resistance, the size of the astrolabe was kept down to
5 or 6 inches in diameter. However, the English navigators preferred
larger ones (6 or 7 inches in diameter) and a wider space between the
sighting vanes on the alidade. By the early seventeenth century the
mariner's astrolabe generally had two quadrants divided into 90-degrees
-- as in the example on the enclosed worksheet.For taking a sight it was suspended by a thread or line -- not
between the thumb and fingers. The navigator used the pair of sighting
holes in the vanes of the alidade for shooting a star. To shoot the sun,
the navigator would hold the astrolabe in such a manner as to allow the
sun's rays to pass through the upper vane, turning the alidade until the
small beam of light fell on the hole of the lower vane.You will find a worksheet for making an astrolabe enclosed in this
packet. You will need to make certain that you have the following
supplies on hand when you begin the project. MATERIALS NEEDED:Crayons
Scissors
Glue
Light weight cardboard or poster board for mounting the pieces of
the astrolabe
Brads or paper fasteners for joining the two completed parts at the
center
Print out and assemble the astrolabe below:
|
